Table of Contents
Have you ever noticed bleeding gums while brushing your teeth? You might want to visit your dentist as soon as possible – It might be a symptom of gum disease. Gum disease is also known as periodontal diseases.
CDC states in the U.S., 47.2% of adults over age 30 have some form of periodontal disease. The periodontal disease mainly occurs in adults. CDC reports next to tooth decay periodontal disease is the biggest threat to dental health. There are two types of gum disease – a) early-stage periodontal disease called Gingivitis, b) Advance stage called Periodontitis.
Cause of Periodontal Disease
Our mouths are full of bacteria – when these bacteria react with tissues surrounding the teeth, causing inflammation in gums resulting in periodontal disease. Plaque is the main villain for every tooth diseases, including periodontal disease. When bacteria stay in the mouth for a longer period, they form a sticky film on teeth called plaque.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) mentions that untreated plaque leads to the formation of tartar – a hardened form of plaque. When tartar spreads to the gum line – which is hard to clean, it eventually leads to inflammation of the gums. If not checked timely, it would turn into periodontal disease.
These diseases not only affect the gums but also affects the strength of teeth. To prevent this, the dentist encapsulates your teeth with a steel crown that holds your teeth together and prevents further decay due to bacteria.
Gingivitis
When the gums become red and swollen, plus blood oozes out while brushing or flossing is gingivitis. It is an early stage and a mild form of periodontal disease. NIH warns that poor oral hygiene is the root cause of gingivitis.
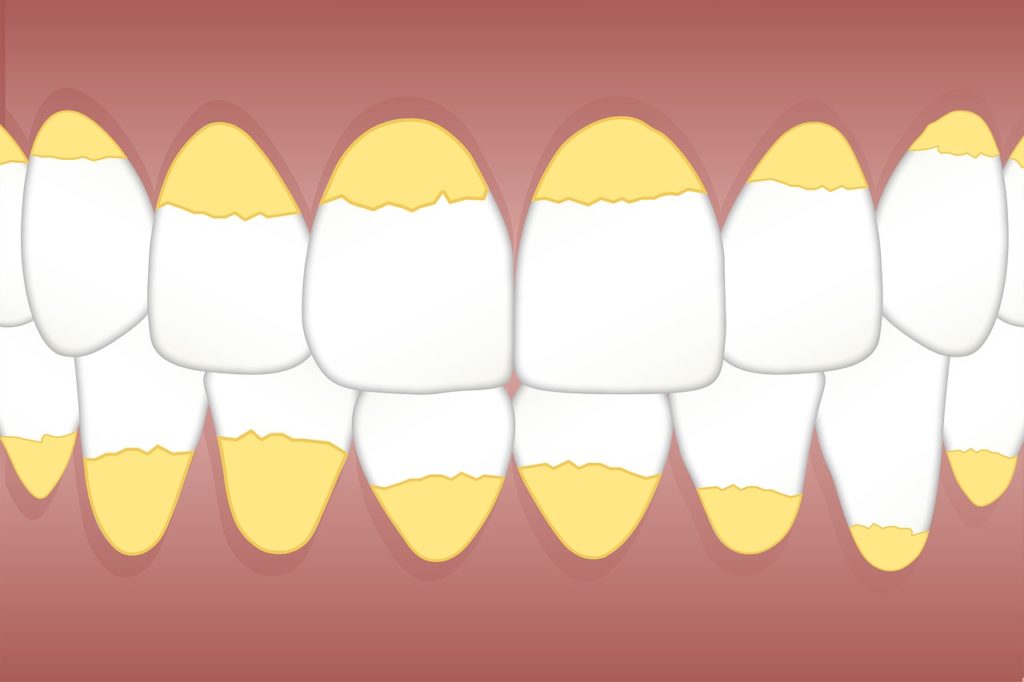
Other causes that could lead to gingivitis –
- Systemic diseases and infections – HIV, Thyroid disorders, and Nutrition deficiency.
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Smoking
- Ill fitted dental appliances like braces.
- Birth control pills
- Hormonal imbalances in pregnancy or puberty could make gum sensitive causing gingivitis.
- Misaligned teeth
- Medications like phenytoin (used for seizure control) and bismuth (used for upset stomach)
Symptoms of gingivitis
Pink colored and firm gums are healthy gums. Gingivitis is not painful – that is the reason many people do not notice the signs of the problem. You have gingivitis when you see symptoms –
- Bad breath
- Swollen gums
- Red or Purple coloration of gums
- Bleeding gums especially when brushing or flossing
- Mouth sores
- Tender and shiny gums
Treatment for gingivitis –
Gingivitis gets better after a professional cleaning followed with proper oral hygiene at home. Professional cleaning might do the work –but if oral care is negligent, it might revert. The dentist will clean the plaque and remove all the tartar. The process is known as scaling.
Over the counter or prescription, toothpaste or mouthwash could help – But not necessarily for severe issues. It is essential to take your dentist or health care provider advice for the treatment.
Periodontitis
Untreated and overlooked gingivitis may lead to a severe stage of periodontal disease –Periodontitis. The condition arises when the inflammation and infection spread out from gums to the supporting bone and ligaments of teeth. Leading to the weakening of bones surrounding teeth, and eventually, the tooth falls out.

NIH explains Periodontitis – inflammation buildup causes an abnormal pocket or gap between teeth and gums. This pocket then fills with more bacteria and plaque or tartar. Interaction with infections and tartar in these pockets leads to damage of tissues and teeth bone. The result is loose of a tooth, gum recession, and bone destruction.
According to the American Academy of Periodontology, there are several types of Periodontitis –
- Chronic Periodontitis – The most common form and in the early stages of Periodontitis. Formation of pockets and gum recession. Common in adults can happen at a young age.
- Aggressive Periodontitis – Bone destruction with rapid loss of gums.
- Periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic disease – It connects with heart diseases, diabetes, and other respiratory conditions. It usually starts at a young age.
- Necrotizing Periodontitis – Seen in systematic conditions like HIV, immunosuppression, and malnutrition – is characterized by lesion formation due to the death of gum tissues, tooth ligaments, and alveolar bones.
Symptoms of Periodontitis –
- Swollen gums
- Red and purple coloration of gums
- Gum recession – teeth appear longer
- Space between teeth increases
- Loose teeth
- Pus around teeth and gums
- Misalignment of teeth while biting
- Bad breath
- Bad taste in the mouth
Treatment for Periodontitis –
According to the American Academy of Periodontology, there are both surgical and non-surgical treatments based on the severity of Periodontitis. You need to visit your dentist for the best treatment suited for your condition. Below are treatments mentioned briefly –
- Non-Surgical treatments – Cleaning of gums, including scaling and root planing.
- Gum graft surgery – Recessed gums are covered by gum grafts to develop gum tissue.
- Regenerative treatments – Includes cleaning of gums and eliminating bacteria in the pockets, promoting natural regeneration of tissues through bone and gum grafts.
- Dental Crown Lengthening
- Dental Implants
- Pocket Reduction Treatments
- Plastic Surgery
Prevention
The best way to prevent gingivitis and Periodontitis is by practicing excellent oral hygiene. The CDC recommends brushing teeth twice a day, followed by flossing. It would be best if you visit your dentist twice a year to keep up with proper oral care. Get your teeth cleaned professionally! Avoid smoking! Smoking is a root cause of many dental problems, including mouth cancer.
From IV sedation to topical anesthetics, the dental anesthesiologist makes use of every sedative according to the patient. All ends up healthy habits! Gum disease originates from poor oral care, and the consequences are severe. It takes no intelligence to understand eating healthy, and keeping healthy habits could save you from all problems. Form a good habit of taking care of your mouth. Teach your kids to practice oral hygiene. If you want your perfect teeth with a beautiful smile, start oral care today!